Share:
Take it offline!
This Education in Motion resource is also available as a printable PDF.
Download PDF
(see Part 1 in previous EIM Resources - September 2019)
Indirect environmental control
A more complex level of environmental control falls inevitably within the scope of domotics, that is, the range of information technology solutions designed for private homes. Domotics aims to create a real "smart home" nervous system, making it more flexible and adaptable to the needs of the home dweller16,17 but in order to enjoy its features a person with disabilities must rely on the interactive modes between the power wheelchair and smartphone/tablet devices that act as intermediaries between the user and the environment. It is therefore extremely important to understand how the power wheelchair and these devices can connect. Connection is achieved by simply equipping the wheelchair with a “Bluetooth module” which very often is also built into the joystick or LCD screen module and which allows the wheelchair and the smartphone to talk to each other. The smartphone detects the wheelchair's Bluetooth module in the same way it would identify a traditional wireless mouse, so that once the devices are paired, it is possible to manage the various settings and gestures with the same controls used to drive the wheelchair. A person with disabilities will just need to see the screen of the smartphone without having to interact directly with it, because all the functions will be accessed through the wheelchair's own control, be it a joystick or a special/alternative input.
Once there is Bluetooth connection between the electronic wheelchair and the smartphone it is possible to manage the house environment in two ways:
- by using an application program (app) managing the Infrared technology Some smartphones have a built-in IR module or can be fitted with one, so that they can operate just like universal remote controls (same as the environmental control modules built into the wheelchair)
- by using an app managing environmental controls through Wi-Fi. Each device (smart TV, video camera, thermostat, etc.) can use a dedicated app but what makes the difference is the possibility to create smart scenarios thanks to an app able to coordinate multiple devices within a network (e.g. Lighting, door locks, video surveillance, thermostats, etc.)
In both cases, the interactive mode between electronic wheelchair and domestic appliances (via Wi-Fi internet connection or via IR) involves an intermediate passage requiring a smartphone/tablet device connected via Bluetooth to the wheelchair; this arrangement can be described as indirect environmental control.
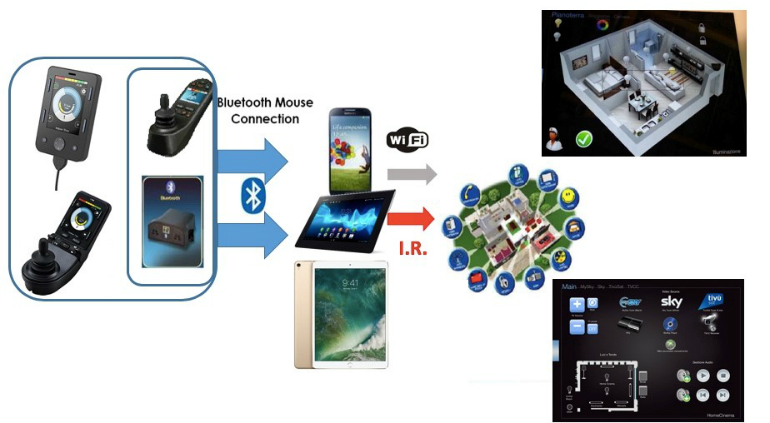
Picture 7: indirect environmental control
Smartphones and tablets are consequently a gateway to the revolutionary world of the “internet of things” (IoT)18 which certainly presents some very interesting aspects that could help improve the safety and independence of people with disabilities. Internet of Things (IoT) is a neologism created in order to give a name to the material world connected via internet; for instance, IoT can refer to a house that opens the windows or turns on the lights and the heating as soon as it knows that the connected device has arrived , or a video surveillance system that sends out warning messages when the alarm is triggered and connects us to the house, or an electronic door lock that opens automatically to provide access to emergency services if the resident needs urgent medical attention. In other words, we are talking about objects that, thanks to a Wi-Fi connection, can link virtual and real world in order to manage actual "smart scenarios". These connections and these scenarios can be personalised to match the needs of people with disabilities, and they are coordinated by apps installed on the smart device operated by the wheelchair control via Bluetooth; some of the most popular apps in this category are Google Home App, iOS Home App, Samsung Smart Home and Smart Home Solution.

Picture 8: representation of IoT (picture taken from www.leseco.ma)
Even the mobility-aid industry has recently become more interested in what IoT has to offer. One example is most certainly the “Remote Seating App” (available for Android and iOS) from Switch-It that can be downloaded for free from the Play Store or Apple Store. It allows smartphones and tablets to receive data from electronic wheelchairs. The app measures and tracks the duration of seating angles in order to improve a client’s overall health through pressure management, especially for high-risk users. The wheelchair connects to the app via a dedicated Bluetooth module (not the same module that was discussed not long ago for climate control) located in a special push-button console of the wheelchair (Switch Box Ctrl5). Thanks to this technology, the wheelchair notifies the user when he or she should change their position. There are both acoustic and visual notifications. The app allows for generating reports (PDFs) that can be shared with the disabled person's healthcare provider as a way of monitoring how pressure is distributed, evaluating efficiency and any changes to be made.

Conclusions
There are currently three broad categories of wheelchair expandable electronics, and they cover almost completely the market for these aids: R-Net P&G, Dynamic, QLogic. For a number of years now, all of these electronic solutions have been able to interact with the mainstream operating systems of ICT devices (Android, iOS, OS X and Windows) but with some distinctive features that must be considered carefully when comparing and choosing a power wheelchair. The various expandable electronics solutions combined with the various operating systems involve significant differences with regards to the pointing, click and gesture functions, which can be extremely important in case of severe disability, especially when it is not possible to install sensors dedicated to some of the functions.
We believe it is essential to find out which ICT devices the user is keen to adopt during the assessment phase leading to the choice of the powerwheelchair. In the same way as power wheelchair driving tests, carried out on increasingly complex tracks, are paramount to highlight the different features and performances of different models and different driving configuration 19, the tests on connectivity and use of smartphones and tablets are definitely an essential step towards choosing the most suitable power wheelchair.
The evaluation of power mobility devices is a complex process, with many factors to consider, concerning both the people with disabilities and their life circumstances, which means that those responsible for evaluating these aids ought to focus on the needs of the person, which must be carefully explored: far from being a waste of time, this is a way to safeguard the right to personal mobility of people with disabilities (art. 19-20 UN Convention on the Rights of Persons with Disabilities, 13 December 2006).